To date, there is no clear, unified method to conduct cumulative impact assessment and management across the EU but some approaches are used depending on the stakeholders involved and the regulatory context:
- Definition of a threshold can be used to define how much an activity impacts biodiversity and thus to place limits on the extent of this activity can be allowed on a given territory. For example, there are cases of Natural Parks imposing limits on wind farm building, such as less than to 300 turbines, on the assumption that a larger installation would have a significant cumulative impact on bird and bat populations.
- Foresight can be a relevant tool to assess the possible future and cumulative impacts and their management for a given territory (see Chapter 4 – Integration of infrastructure into the landscape).
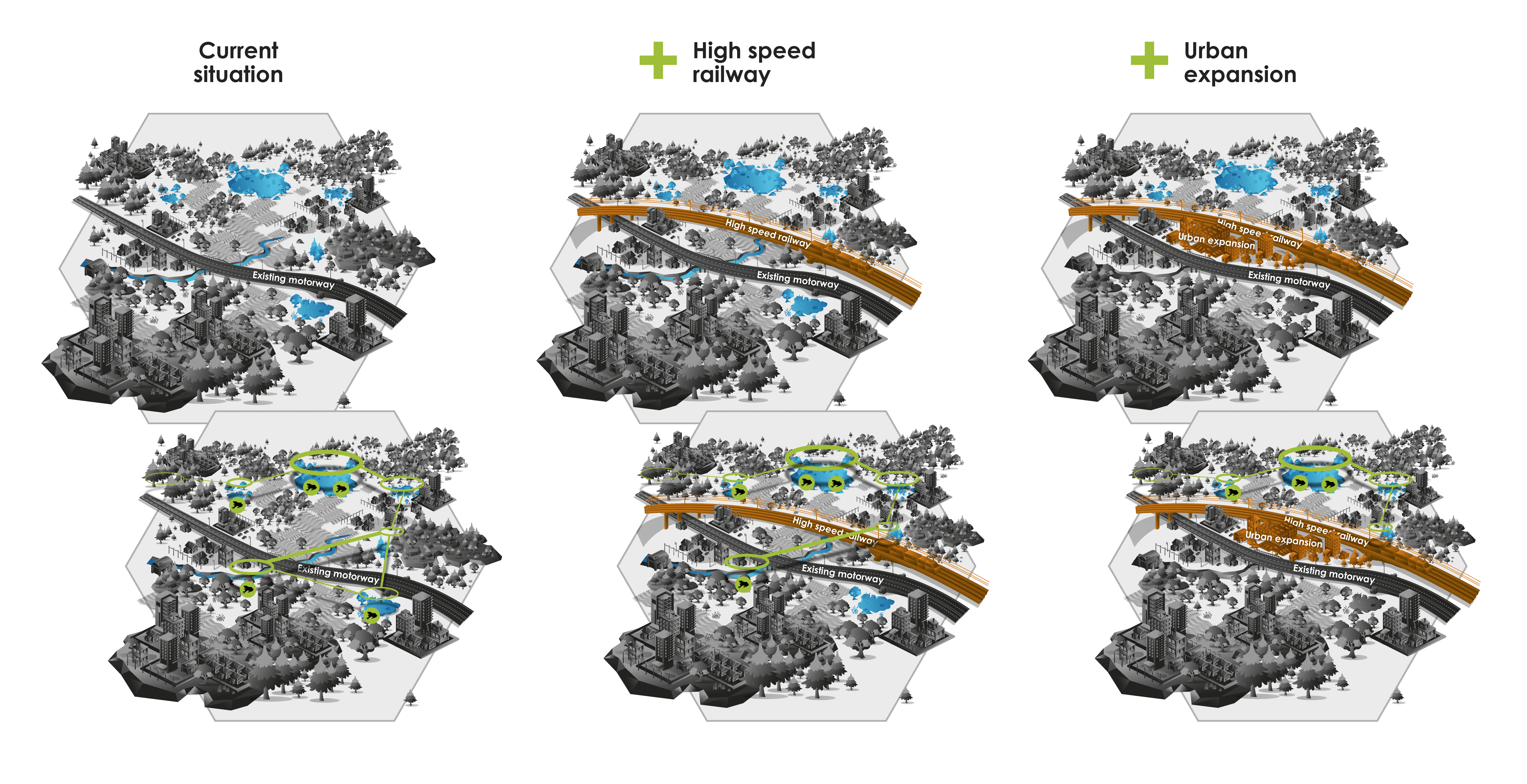
- Predict cumulative impacts through modelling: ecological modelling is used to assess scenarios and evaluate the contribution of multiple landscape elements, including transport infrastructure, on species dynamics (Figure 3.5.1). Such a modelling-based approach can be extended to multiple species and different areas of biodiversity and has been implemented in several studies.